Central banks resort to monetary policy to achieve price stability. The effectiveness of such policies in relation to inflationary pressure in 2021-2022 has become the subject of intense discussion in academic circles.
In response to an 8.4% price increase in 2022, the European Central Bank tightened monetary policy for the first time in more than a decade, ending the era of negative policy rates in the Eurozone. This European Central Bank policy aims to return inflation to the target level of 2 percent.
The following article reviews the increase in price levels in Georgia in 2021-2022 and the monetary policy adopted by the National Bank as a response. By analyzing the causes of inflation, we will try to assess the efficiency of monetary policy. In addition, we will discuss alternative means of reducing inflation.
What should we know?
Monetary policy plays a critical role in reducing demand-driven inflation but is less effective when dealing with supply-driven inflation. In the latter case, the increase in price level is mainly related to production costs or supply chain disruption. Monetary policy, which primarily focuses on managing money and interest rates, is not effective against such factors.
The National Bank of Georgia responded to inflation in 2021-2022 by gradually tightening monetary policy, increasing the refinancing rate from 8 to 11 percent (Figure N1), even though the causes of inflation in this period were different from one another.
Figure N1: Changes in the monetary policy rate
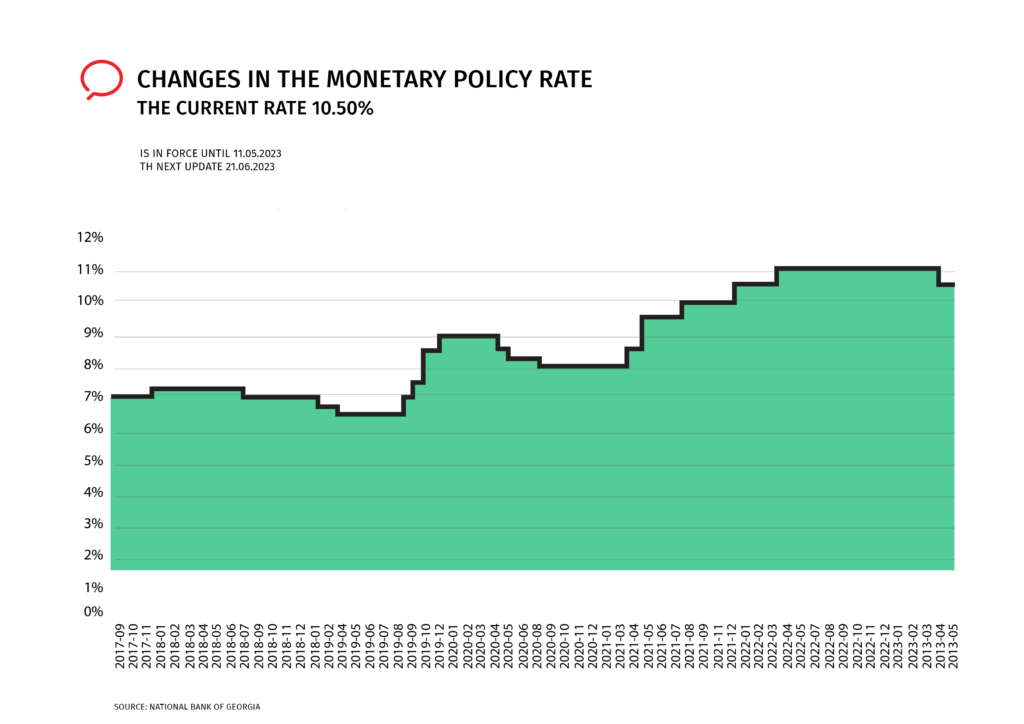
For more details, see the following article: The Causes of inflation in Georgia
Why should I be interested in this topic?
● In Georgia, the years 2021-2022 were characterized by high inflation. A sharp increase in prices began in the second half of 2021, and a record-breaking inflation rate of 13.9 percent was documented in December. The biggest contribution to inflation was attributed to the rise in prices of imported food and fuel. Inflation remained high (11.9%) in 2022 as well. During this period, the price of apartment rent, locally manufactured goods, and services increased. This was mainly due to the increase in demand and spending by Russian immigrants.
● Thus, the price increase in Georgia was attributed to a contraction in supply in 2021, and an increase in demand starting from 2022.
● Low-income families have been most affected by inflation since a large portion of their income is spent on food, transportation, and housing. Since 2021, the prices of such goods and services have increased the most.
● In this context, monetary policy tightened by the National Bank of Georgia, which makes money more expensive and hinders economic activity, contributes to the growing disparity between natives' and immigrants' purchasing power.
For more details, see the following article: What is inflation and how is it calculated?
Our comment
Monetary policy is ineffective against supply shocks. Tight monetary policy can only reduce inflation caused by the increase in immigrants' demand at the expense of the local population's consumption capacity and the deterioration of export potential. Therefore, it is necessary to implement alternative ways of easing inflation.
Structural reforms, infrastructural investments, increase in educational investments, and strengthening anti-monopoly policy are relatively effective against supply-driven inflation. It is also of fundamental importance to strengthen the local economy and decrease the trade deficit, in order to diminish dependence on imports and subsequently alleviate imported inflation..
In more details:
A strict monetary policy eases inflation by reducing demand. The most crucial channels through which monetary policy influences inflation in Georgia are interest rates and exchange rates:
● The tightening of monetary policy increases bank loan interest rates. Under these conditions, demand for loans decreases, resulting in lower investment and consumer spending. Ultimately, this process suppresses demand and contributes to reducing the price levels.
● The increase in the interest rate on local assets (in national currency) contributes to an increase in demand, which leads to the strengthening of the GEL. The strengthening of the exchange rate reduces imported goods prices and increases the price of exported goods. As a result, the price level of imported goods decreases. In addition, the strengthening of the local currency contributes to the growth of imports and the decrease in exports. This reduces aggregate demand and, accordingly, inflation.
As a result of both mechanisms, monetary policy suppresses inflation by reducing demand. However, the causes of inflation are not always related to the increase in demand.
Main causes of inflation in 2021-2022:
The causes of the increased inflation from the second half of 2021 were initially related to the global increase in fuel and food prices. A global increase in inflation also indicates such an occasion. As Georgia is an import-dependent country, the increased prices of food and fuel were transferred to us as imported inflation (Figure N2).
Figure N2: Imported and Domestic Inflation
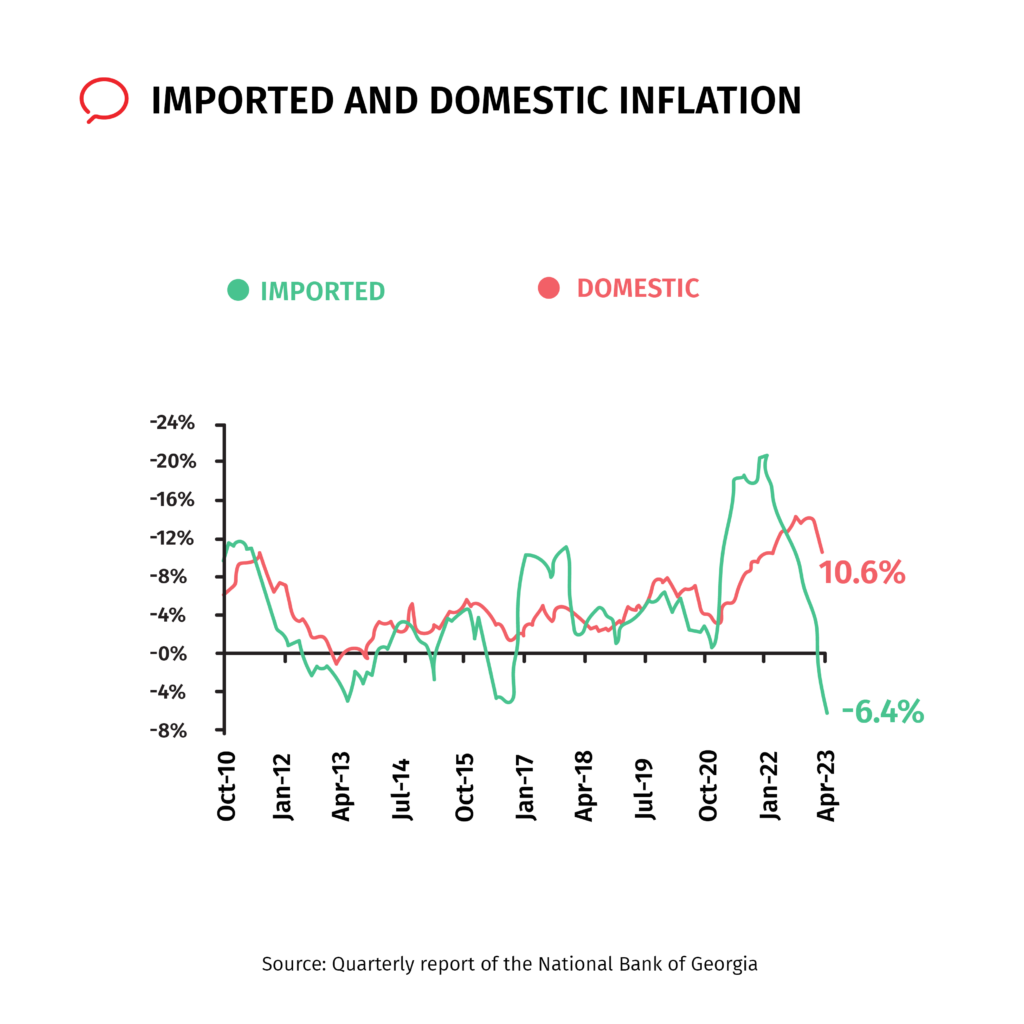
The monetary policy tightened by the National Bank of Georgia in response to inflation is ineffective against these reasons. This is because the problem lies not in increased demand, but in decreased supply. Hindering the supply side was first related to Covid regulations and then to the Russia-Ukraine war.
Figure N2 also shows that from 2022, imported inflation decreases, but domestic inflation remains high. This indicates excessive demand given immigration flows and a fast-growing economy. Strict monetary policy will also be less effective in this case. This is because the increase in demand is related to the increase in expenses incurred by immigrants, not locals. Besides, limited access to credit as a result of stricter interest rates puts locals at a disadvantage compared to immigrants.
At the end of 2022, amid rising inflation, nominal wages also increased, sparking discussions about whether a wage-price spiral is taking place. The essence of the matter lies in what actually causes inflation - price increases or wage increases. On the one hand, an increase in wages leads to an increase in disposable income, an increase in demand, and, accordingly, an increase in the price level. On the other hand, increasing prices cause employees to demand salary increases. This results in an increase in production costs, which, in turn, leads to an increase in the prices of final goods and services. Thus, theoretically, both factors can cause inflation. However, in rare cases, wage growth can be the primary cause of inflation, and there is already consensus around the world that wage increases should not be held back due to fear of inflation. Moreover, especially in oligopolistic markets, companies may raise product prices to increase profits. In the case of Georgia, the wage-inflation spiral is not identified, and fighting inflation by reducing wages will be a futile strategy, which at the same time will further exacerbate the socio-economic condition of the population.
Alternative policy against inflation
A quick and complete solution to these supply problems is unlikely. Therefore, it is necessary to consider alternative policies against supply-driven inflation:
● To reduce imported inflation, it is necessary to reduce imports and encourage exports by developing domestic production. This requires structural reforms, infrastructure investments, industrial policies, and increased investment in education. Strict monetary policy, on the contrary, obstructs economic activity, increases imports, and decreases exports. As a result, the country's economy becomes more vulnerable to global inflation shocks.
● To deal with problems caused by increased inflation due to immigrant spending, it is possible, for example, to impose a ceiling on rent prices. German government resorted to such measures during the immigration influx in 2015-16. Policies aimed at increasing labor market competitiveness will also work effectively.
● Price increases resulting from increased profit margins are associated with a lack of competition and the oligopolistic nature of markets. Therefore, it should be resolved by the National Competition Agency with an anti-monopoly policy. In this case, monetary policy reduces workers' wage bargaining power, further increasing inflationary pressures on low-income earners.
The article was prepared with the support of Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung. The views expressed in this publication are not necessarily those of the Friedrich-Ebert Stiftung. Commercial use of all media published by the Friedrich-Ebert-Stiftung (FES) is not permitted without the written consent of the FES.














